I am a third year PhD student at Renmin University of China, under supervision of Prof. Jing Zhang. Currently, my research focuses on Tool Intelligence of LLMs, AI4Research and Academic Data Mining.
Besides, I love soccer⚽️, photography📷, and snowboarding🏂.
I also keep training for Triathlon races 🏊 🚴 🏃 and Marathon races 🏃♂️.
Feel free to chat with me for our shared interests whether in research or life.
Industry Experience
Academic Service
What’s New!
- 🔔 SoAy has been accepted by KDD’25. Appreciation to all the coauthors! - Nov 2024
- 🔔 R-Eval has been accepted by KDD’24. Appreciation to all the coauthors! - May 2024
Publications
2025
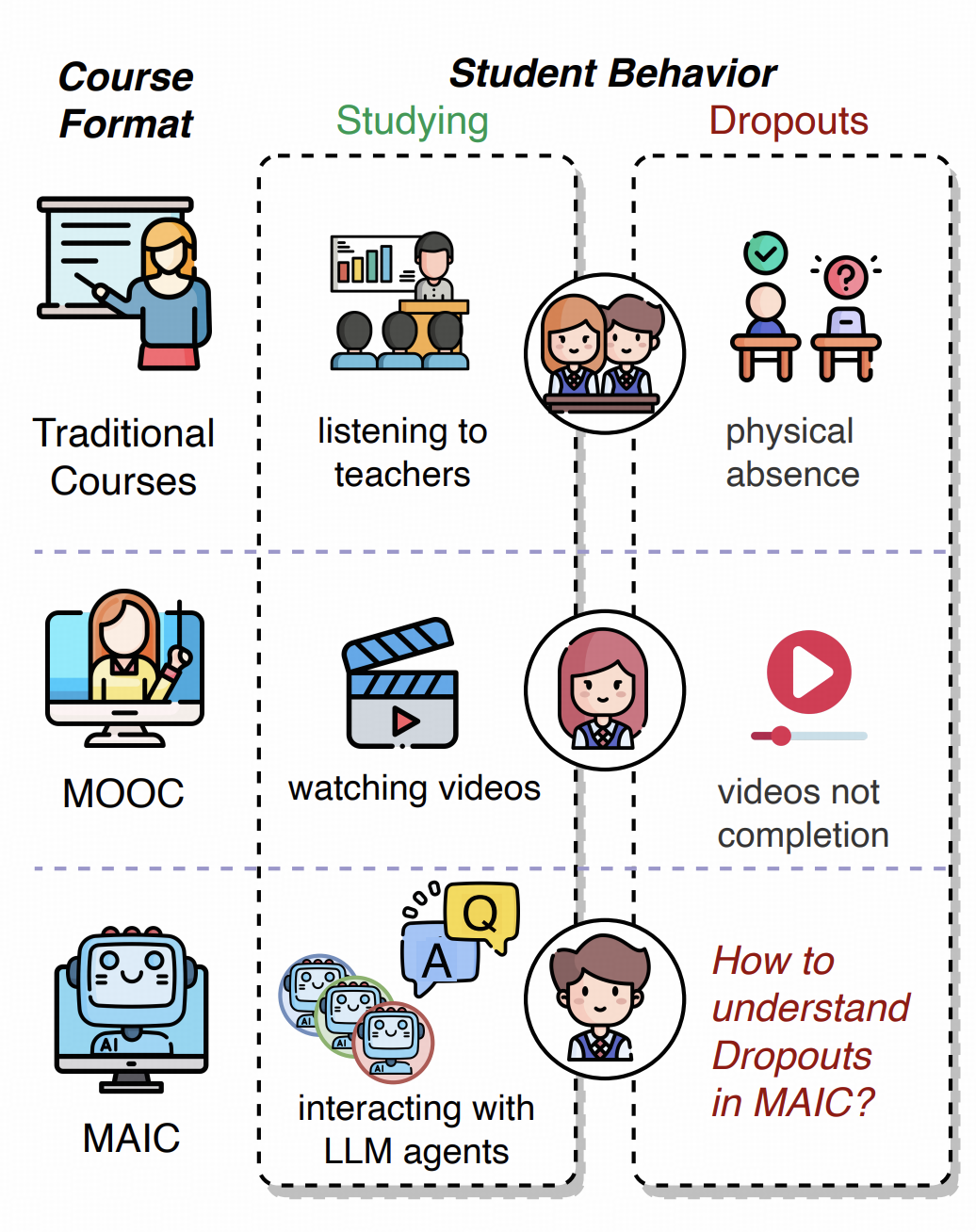
Handling Students Dropouts in an LLM-driven Interactive Online Course Using Language Models
[PDF]
Yuanchun Wang, Yiyang Fu, Jifan Yu, Daniel Zhang-li, Zheyuan Zhang, Joy Lim Jia Yin, Yucheng Wang, Peng Zhou, Jing Zhang, Huiqin Liu
Interactive online learning environments, represented by Massive AI-empowered Courses (MAIC), leverage LLM-driven multi-agent systems to transform passive MOOCs into dynamic, text-based platforms, enhancing interactivity through LLMs. This paper conducts an empirical study on a specific MAIC course to explore three research questions about dropouts in these interactive online courses: (1) What factors might lead to dropouts? (2) Can we predict dropouts? (3) Can we reduce dropouts?
[PDF]
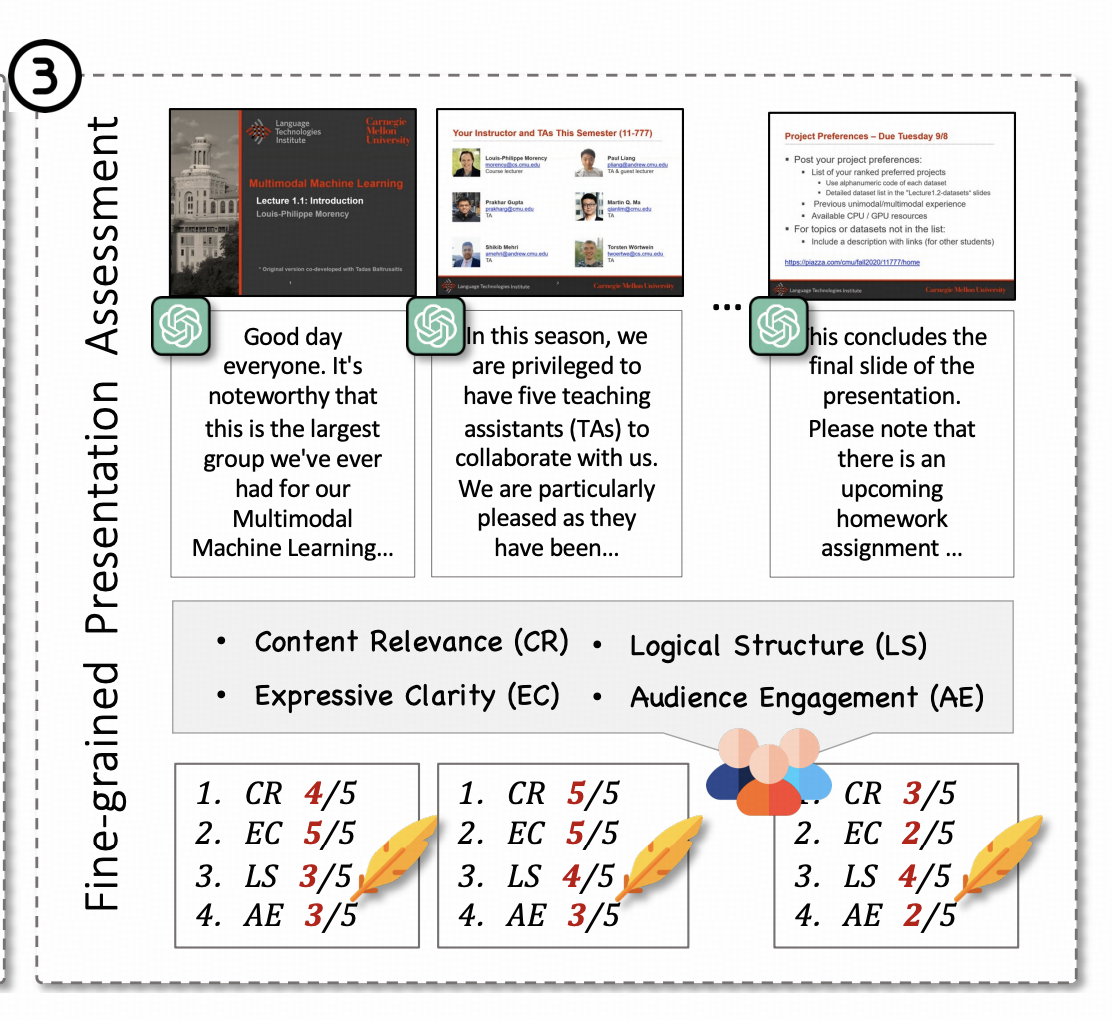
Joy Lim Jia Yin, Daniel Zhang-Li, Jifan Yu, Haoxuan Li, Shangqing Tu, Yuanchun Wang, Zhiyuan Liu, Huiqin Liu, Lei Hou, Juanzi Li, Bin Xu
In this paper, we introduce LecEval, an automated metric grounded in Mayer's Cognitive Theory of Multimedia Learning, to evaluate multimodal knowledge acquisition in slide-based learning. LecEval assesses effectiveness using four rubrics: Content Relevance (CR), Expressive Clarity (EC), Logical Structure (LS), and Audience Engagement (AE).
2024
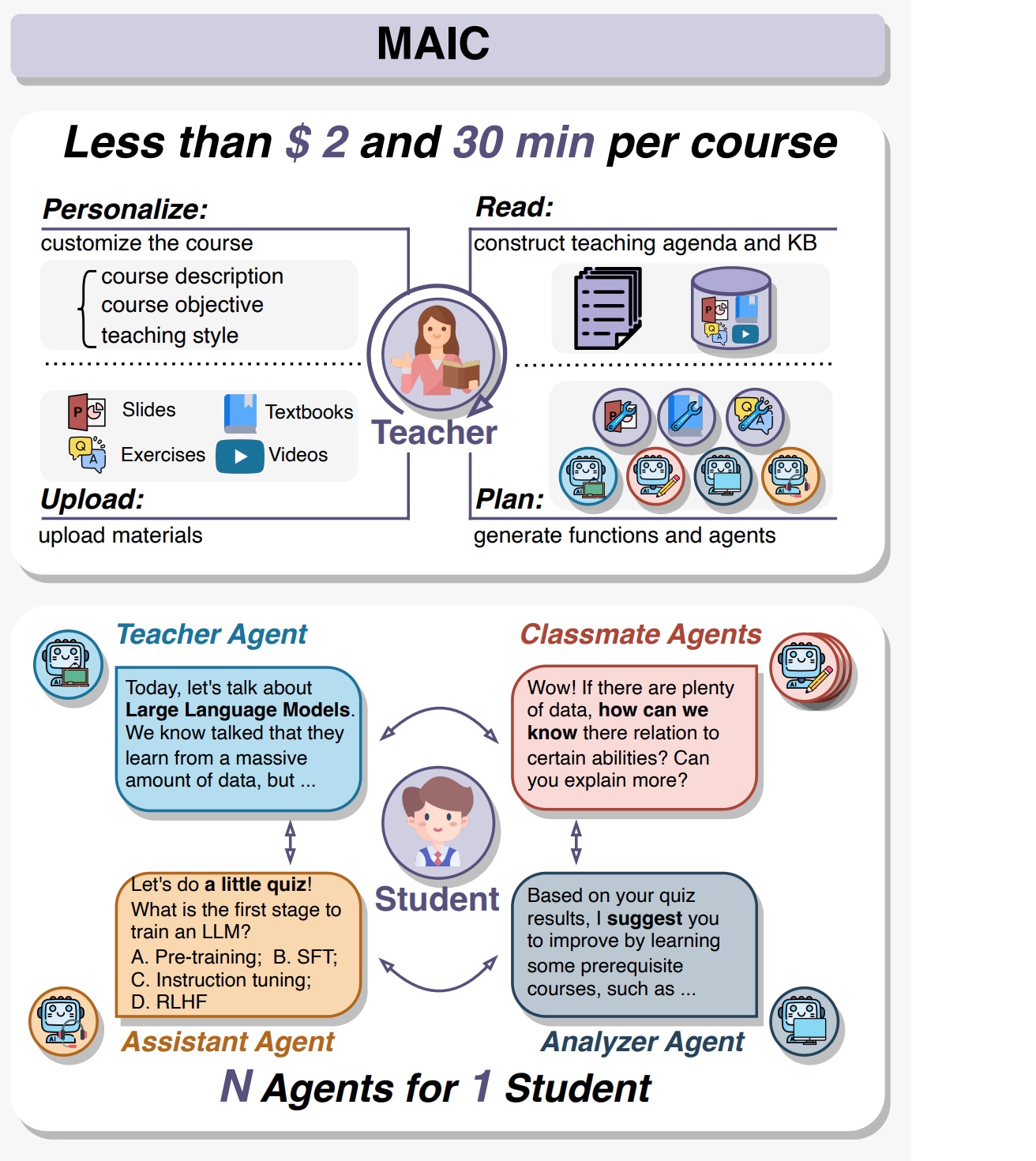
From MOOC to MAIC: Reshaping Online Teaching and Learning through LLM-driven Agents
[PDF]
Jifan Yu, Zheyuan Zhang, Daniel Zhang-li, Shangqing Tu, Zhanxin Hao, Rui Miao Li, Haoxuan Li, Yuanchun Wang, Hanming Li, Linlu Gong, Jie Cao, Jiayin Lin, Jinchang Zhou, Fei Qin, Haohua Wang, Jianxiao Jiang, Lijun Deng, Yisi Zhan, Chaojun Xiao, Xusheng Dai, Xuan Yan, Nianyi Lin, Nan Zhang, Ruixin Ni, Yang Dang, Lei Hou, Yu Zhang, Xu Han, Manli Li, Juanzi Li, Zhiyuan Liu, Huiqin Liu, Maosong Sun
MAIC (Massive AI-empowered Course) is a new form of online education that leverages LLM-driven multi-agent systems. The teacher, assistants and even classmates in traditional classrooms are replaced by LLM Agents. In MAIC, every student is envolved in a personal virtual classroom and given a unique learning experience. This project will continue to evolve, ultimately aiming to establish a comprehensive open platform that supports and unifies research, technology, and applications in exploring the possibilities of online education in the era of large model AI to construct an AI-augmented classroom, balancing scalability with adaptivity.
[KDD'24] R-Eval: A Unified Toolkit for Evaluating Domain Knowledge of Retrieval Augmented Large Language Models
[code], [PDF]
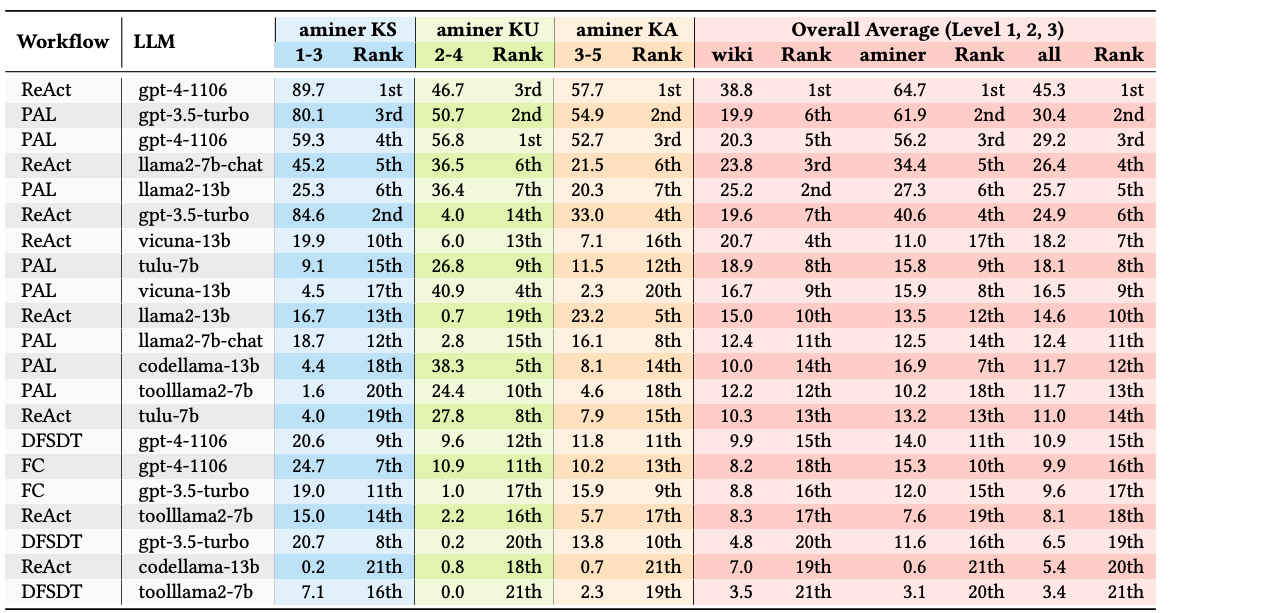
Shangqing Tu * and Yuanchun Wang *, Jifan Yu, Yuyang Xie, Yaran Shi, Xiaozhi Wang, Jing Zhang, Lei Hou, Juanzi Li
A Python toolkit designed to streamline the evaluation of different RAG workflows in conjunction with LLMs. Our toolkit, which supports popular built-in RAG workflows and allows for the incorporation of customized testing data on the specific domain. * User-friendly: R-Eval provides easy-to-use scripts for running and analysing experiments with the given models and datasets automatically. * Modular: R-Eval is designed to be modular, which allows users to easily extend the framework with new models, datasets, and analysis tools. * Extensibility: The domain-agnostic design of R-Eval makes it easy to evaluate Retrieval Augmented Large Language Models on new domain based on our framework.
[code], [PDF], [System], [Application], [Model], [Benchmark & Dataset]
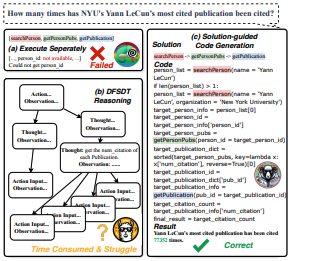
Yuanchun Wang, Jifan Yu, Zijun Yao, Jing Zhang, Yuyang Xie, Shangqing Tu, Yiyang Fu, Youhe Feng, Jinkai Zhang, Jingyao Zhang, Bowen Huang, Yuanyao Li, Huihui Yuan, Lei Hou, Juanzi Li, Jie Tang
A solution-based LLM API-using methodology for academic information seeking, which is named SoAy. It uses code with a solution as the reasoning method, where a solution is a pre-constructed API calling sequence. The addition of the solution reduces the difficulty for the model to understand the complex relationships between APIs. Code improves the efficiency of reasoning. To evaluate SoAy, we introduce SoAyBench, an evaluation benchmark accompanied by SoAyEval, built upon a cloned environment of APIs from AMiner.
2023
[AI Open] Authorship style transfer with inverse transfer data augmentation
[code], [PDF]
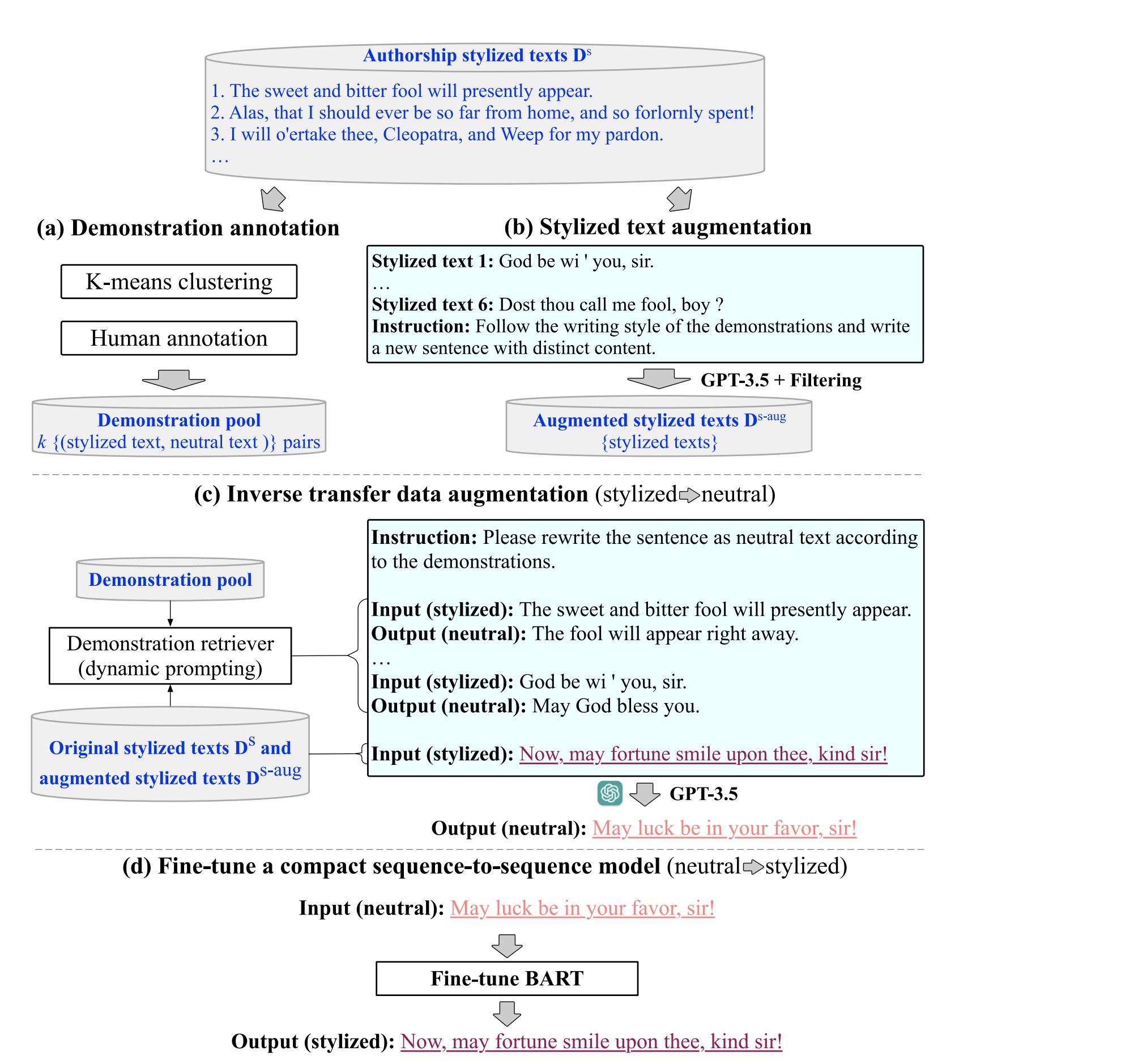
Zhonghui Shao, Jing Zhang, Haoyang Li, Xinmei Huang, Chao Zhou, Yuanchun Wang, Jibing Gong, Cuiping Li, Hong Chen
Authorship style transfer aims to modify the style of neutral text to match the unique speaking or writing style of a particular individual. This paper proposes an inverse transfer data augmentation (ITDA) method, leveraging LLMs to create (neutral text, stylized text) pairs. This method involves removing the existing styles from stylized texts, a process made more feasible due to the prevalence of neutral texts in pre-training. We use this augmented dataset to train a compact model that is efficient for deployment and adept at replicating the targeted style. Our experimental results, conducted across four datasets with distinct authorship styles, establish the effectiveness of ITDA over traditional style transfer methods and forward transfer using GPT-3.5.
[ACL'23] GKD: A General Knowledge Distillation Framework for Large-scale Pre-trained Language Model
[code], [PDF]
Shicheng Tan, Weng Lam Tam, Yuanchun Wang, Wenwen Gong, Shu Zhao, Peng Zhang, Jie Tang
A general knowledge distillation framework that supports distillation on larger-scale PLMs using various distillation methods. With GKD, developers can build larger distillation models on memorylimited GPUs and easily switch and combine different distillation methods within a single framework. Experimental results show that GKD can support the distillation of at least 100B-scale PLMs and 25 mainstream methods on 8 NVIDIA A100 (40GB) GPUs.
[code], [PDF]
Shicheng Tan, Weng Lam Tam, Yuanchun Wang, Wenwen Gong, Shu Zhao, Peng Zhang, Jie Tang
A general language model distillation (GLMD) method that performs two-stage word prediction distillation and vocabulary compression, which is simple and surprisingly shows extremely strong performance. Specifically, GLMD supports more general application scenarios by eliminating the constraints of dimension and structure between models and the need for labeled datasets through the absence of intermediate layers and golden labels. Meanwhile, based on the long-tailed distribution of word frequencies in the data, GLMD designs a strategy of vocabulary compression through decreasing vocabulary size instead of dimensionality.
2022
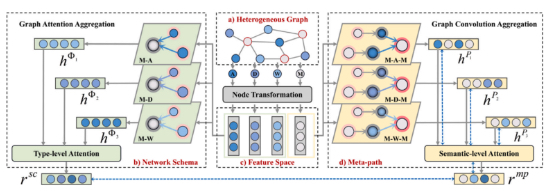
[KBS] NHGMI: Heterogeneous graph multi-view infomax with node-wise contrasting samples selection
[code], [PDF]
Qing Li, Hang Ni and Yuanchun Wang
A novel unsupervised method for heterogeneous graph representation learning, rooted in the principles of mutual information maximization. NHGMI comprehensively harnesses the inherent characteristics of HINs and adeptly amalgamates diverse semantic information emanating from multiple contrasting perspectives. In addition to inter-view contrasts, NHGMI also incorporates intra-view contrasts. Diverging from conventional contrastive learning approaches, NHGMI meticulously selects contrasting samples based on similarity metrics, thereby achieving a noise-free contrastive learning paradigm.